Coconuts
Coconuts are the fruit of the coconut palm tree, which is found in tropical coastal regions. Coconut can be consumed in a variety of ways, including fresh or dried, as coconut water, coconut milk, or coconut oil. This article refers to dried (desiccated) coconut.
What is the nutrient content of coconut?
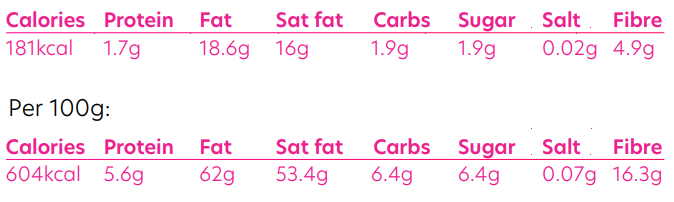
A recommended serving size of coconut is 30g, which is roughly 3 tablespoons of shredded or flaked coconut:

What are the health benefits of coconut?
1. Energy and Metabolism: Coconut contains medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs), a type of fat that the body metabolizes differently from other fats. MCTs are quickly absorbed and can be used as a quick energy source
2. Digestive Health: The high fibre content in coconut promotes healthy digestion and can help prevent constipation.
3. Antimicrobial Properties: Lauric acid, a type of saturated fat in coconut, has been shown to have antimicrobial properties, which can help protect against certain infections
Where can I find coconut?
Dried coconut can be eaten on its own, or as part of many sweet and savoury dishes, such as coconut macaroons, trail mixes, cereal bars, and curries.

References:
Public Health England (2016). Government Dietary Recommendations. Available at:
https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/media/5a749f
ece5274a44083b82d8/government_dietary_recomme
ndations.pdf [Accessed 8 November 2024].
National Health Service (2022). 5 A Day portion sizes. Available at:
https://www.nhs.uk/live-well/eat-well/5-a-day/portio
n-sizes/ [Accessed 10 September 2024].
Jadhav, H. B., & Annapure, U. S. (2023). Triglycerides of medium-chain fatty acids: a concise review. Journal of food science and technology, 60(8), 2143–2152. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-022-05499-w
[Accessed 10 September 2024].
Cronin P, Joyce SA, O’Toole PW, O’Connor EM. Dietary Fibre Modulates the Gut Microbiota. Nutrients. 2021;13(5):1655. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13051655
[Accessed 10 September 2024]
Written By:
Grace Williams, Head of Nutrition & Operations, myfood24.











 Back to knowledge library
Back to knowledge library