Calcium
What is Calcium?
Calcium is the most abundant mineral in the body and is found in many foods such as milk, soya drinks, cheese and sardines. This mineral makes up some structures in the body including bones and teeth meaning a lack of calcium throughout life could lead to osteoporosis in later life. The UK government recommends a calcium intake of 700 mg per day for adults. For example eating 20g cheddar cheese, 20g pesto sauce, 100g sausages and 250ml skimmed milk would meet this daily target intake.

What is the role of Calcium?
Calcium is involved in maintaining healthy bones and teeth as well as supporting the normal function of nerves, muscles and blood clotting. Calcium can be stored in the body within the bones. Calcium absorption can be helped by the presence of Vitamin D in the body and hindered to a small extent by caffeine.
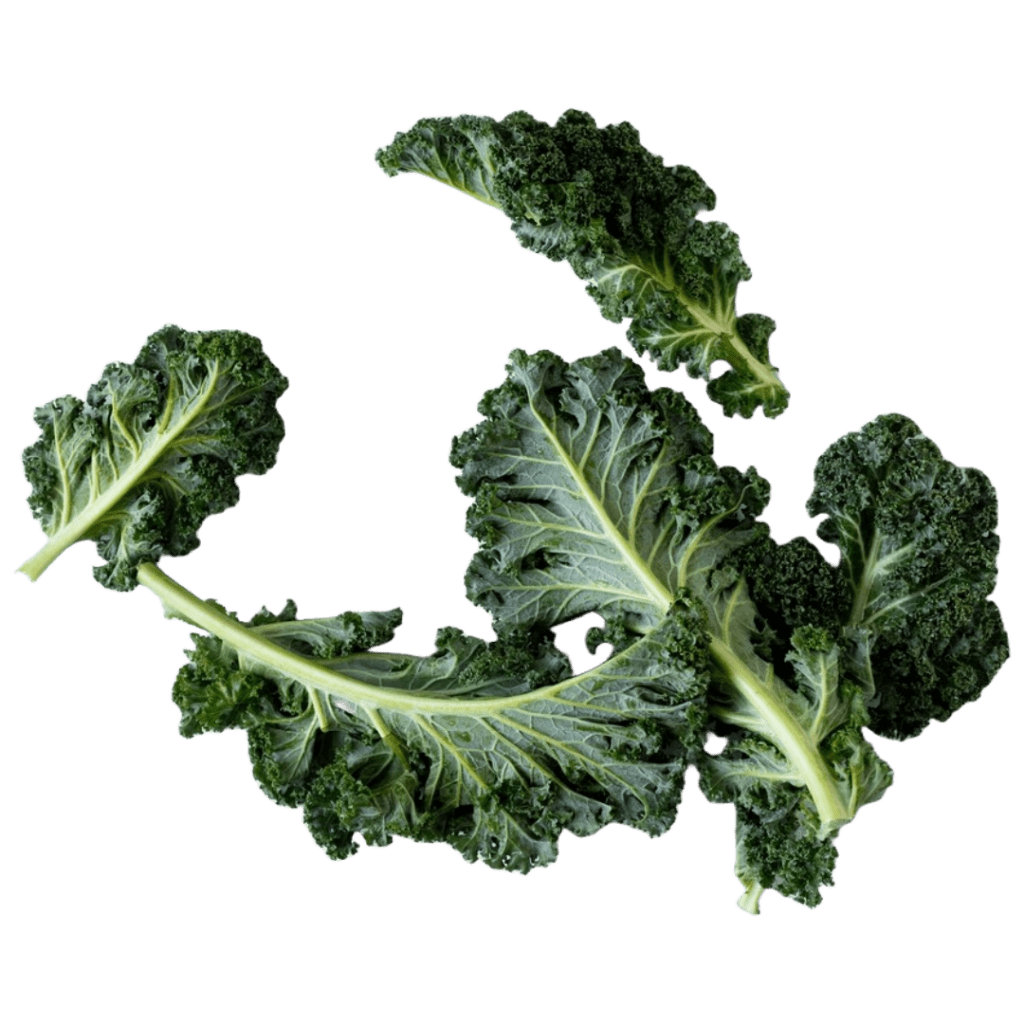
What foods contain Calcium?
Foods rich in calcium include milk, cheese, and other dairy, green leafy vegetables like kale and okra, fortified soya drinks, fortified flours, fish with bones like sardines and pilchards. The recommended intake of calcium can be achieved through a healthy, balanced and varied diet.

Further Resources:
References:
Public Health England (2016). Government Dietary Recommendations: Government recommendations for energy and nutrients for males and females aged 1 –18 years and 19+ years. Available at: https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/media/5a749fece5274a44083b82d8/government_dietary_recommendations.pdf [Accessed 21 Aug 2024].
National Health Services (2020). Calcium: Vitamins and minerals. Available at: https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/vitamins-and-minerals/calcium/ [Accessed 10 September 2024].
National Institutes of Health (2024). Calcium. Available at: https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Calcium-HealthProfessional/ [Accessed 10 September].
Written By:
Lucy Clarkson, SENR Nutritionist and Database Support, myfood24.








 Back to knowledge library
Back to knowledge library