Currants
Currants are small, dried berries that typically come from the Zante grape. They may be confused with fresh currants, such as blackcurrants and redcurrants, which are different types of fruits.
What is the nutrient content of Currants?
A recommended serving size of currants is one heaped tablespoon, or around 30g:
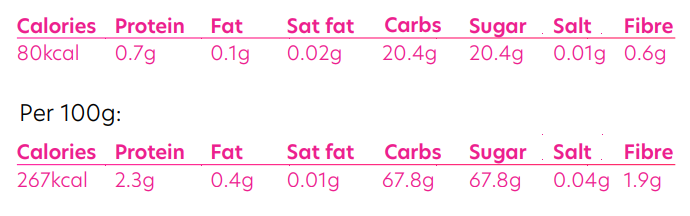

What are the health benefits of Currants?
1. High in Antioxidants: Currants contain high levels of polyphenols and flavonoids, which have powerful antioxidant properties that help protect cells from oxidative damage.
2. Heart Health: The potassium content in currants supports heart function, protects against heart disease, and helps regulate blood pressure.
3. Iron: Currants are a source of iron, supporting red blood cell production and contributing to energy levels.
Where can I find Currants?
Currants can be eaten on their own as a snack. They can also be found in traditional British bakery products, such as scones, fruitcake, and Eccles cakes, and in Middle Eastern and Mediterranean savoury dishes, such as pilaffs, tagines, and stuffings.

References:
Public Health England (2016). Government Dietary Recommendations. Available at:
https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/media/5a749f
ece5274a44083b82d8/government_dietary_recomme
ndations.pdf [Accessed 8 November 2024].
National Health Service (2022). 5 A Day portion sizes. Available at:
https://www.nhs.uk/live-well/eat-well/5-a-day/portio
n-sizes/ [Accessed 10 September 2024].
Abouzeed, Y. M., Zgheel, F., Elfahem, A. A., Almagarhe, M. S., Dhawi, A., Elbaz, A., Hiblu, M. A., Kammon, A., & Ahmed, M. O. (2018). Identification of phenolic compounds, antibacterial and antioxidant activities raisin extracts. Open veterinary journal, 8(4), 479–484.
https://doi.org/10.4314/ovj.v8i4.20 [Accessed 10 September 2024].
Anderson, J. W., & Waters, A. R. (2013). Raisin consumption by humans: effects on glycemia and insulinemia and cardiovascular risk factors. Journal of food science, 78 Suppl 1, A11–A17.
https://doi.org/10.1111/1750-3841.12071 [Accessed 10 September 2024].
Olmo-Cunillera, A., Escobar-Avello, D., Pérez, A. J.,
Marhuenda-Muñoz, M., Lamuela-Raventós, R. M., &
Vallverdú-Queralt, A. (2019). Is Eating Raisins
Healthy?. Nutrients, 12(1), 54.
https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12010054 [Accessed 10
September 2024]
Written By:
Grace Williams, Head of Nutrition & Operations, myfood24.











 Back to knowledge library
Back to knowledge library